Bring in the Germans: The Fate of the Losers at the Paris Peace Conference
Manage episode 328917900 series 3350741
The most important task at the 1919 Paris Peace Conference was the drafting of peace terms for the losers of the war. Germany and Austria assumed Woodrow Wilson would insist on a fair, respectful compromise peace based on the Fourteen Points. So they were shocked when the Treaty of Versailles demanded territory, demilitarization, and reparations. Is this what caused World War II?
Show Notes
The story about the police horse in Vienna is recounted by author Margaret MacMillan, author of the book Paris 1919: Six Months That Changed the World, in a 2007 speech to the National World War I Museum. MacMillan's speech, like her book, is fantastic--you can see it here.
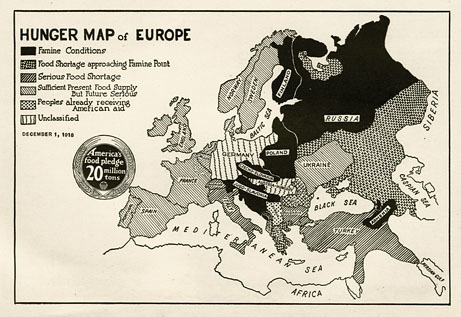
This map depicts the hunger levels of Europe in December 1918. It was created by the US Food Administration in cooperation with the Department of Agriculture and the Bureau of Education. Germany and Austria-Hungary (which, in fact, no longer existed) were labeled "Unclassified" because when this map was prepared, two two countries were still classified as enemies and the food blockade was still in effect. Austria, at least, would have fallen into the black zone.
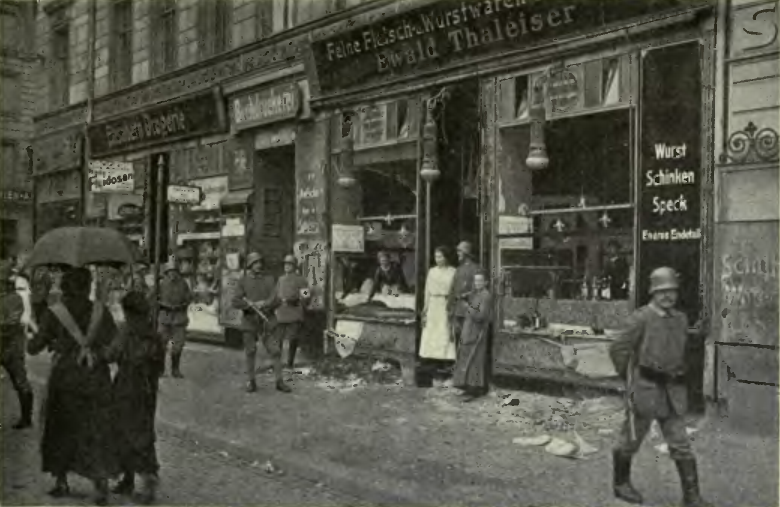

Food riots became common across the Central Powers countries. This photo depicts a delicatessan in Berlin that has been looted by a mob.

This cartoon, published in 1917 in the Österreichische Volkszeitung, is about the food conflict between Austria and Hungary. The Austrian part of the Habsburg Empire ("Cis") is represented by the Viennese Mayor Richard Weiskirchner (1861-1926) and the Federal Minister of Food Anton Höfer begging for food deliveries. On the other side of the river Leitha, the Hungarian part ("Trans") is shown as a fat man stone-heartedly withholding his herd of animals and boxes of supplies. This cartoon reflects Viennese popular sentiment toward Hungarians, who they believed were selfishly withholding critical supplies. In fact, Hungary did restrict shipments to Austria in order to safeguard food for its own people. However, the attitude of paranoia extended to numerous ethnic groups and poisoned relations between the multiple nationalities of the Austro-Hungarian empire.

German Quartermaster General Erich Ludendorff fully understood that his troops had been defeated in late September 1918. This diary entry by a German General Staff officer makes it clear that Ludendorff had no illusions about Germany's ability to go on fighting. However, by the spring of 1919, Ludendorff had convinced himself that the army had never been truly defeated in battle. Instead, the military had been betrayed by sinister forces at home, most likely Communists and Jews.
The Fry and Laurie sketch on the Treaty of Westphalia is pure fantasy--no, Luxembourg was not divided between Sweden and France--but it accurately depicts the attitude of diplomats for most of European history. To the winners of war went the spoils, and never mind what the people who actually lived there thought about the matter. You can watch the entire sketch, which was originally broadcast on BBC 1 in January 2000, on YouTube.
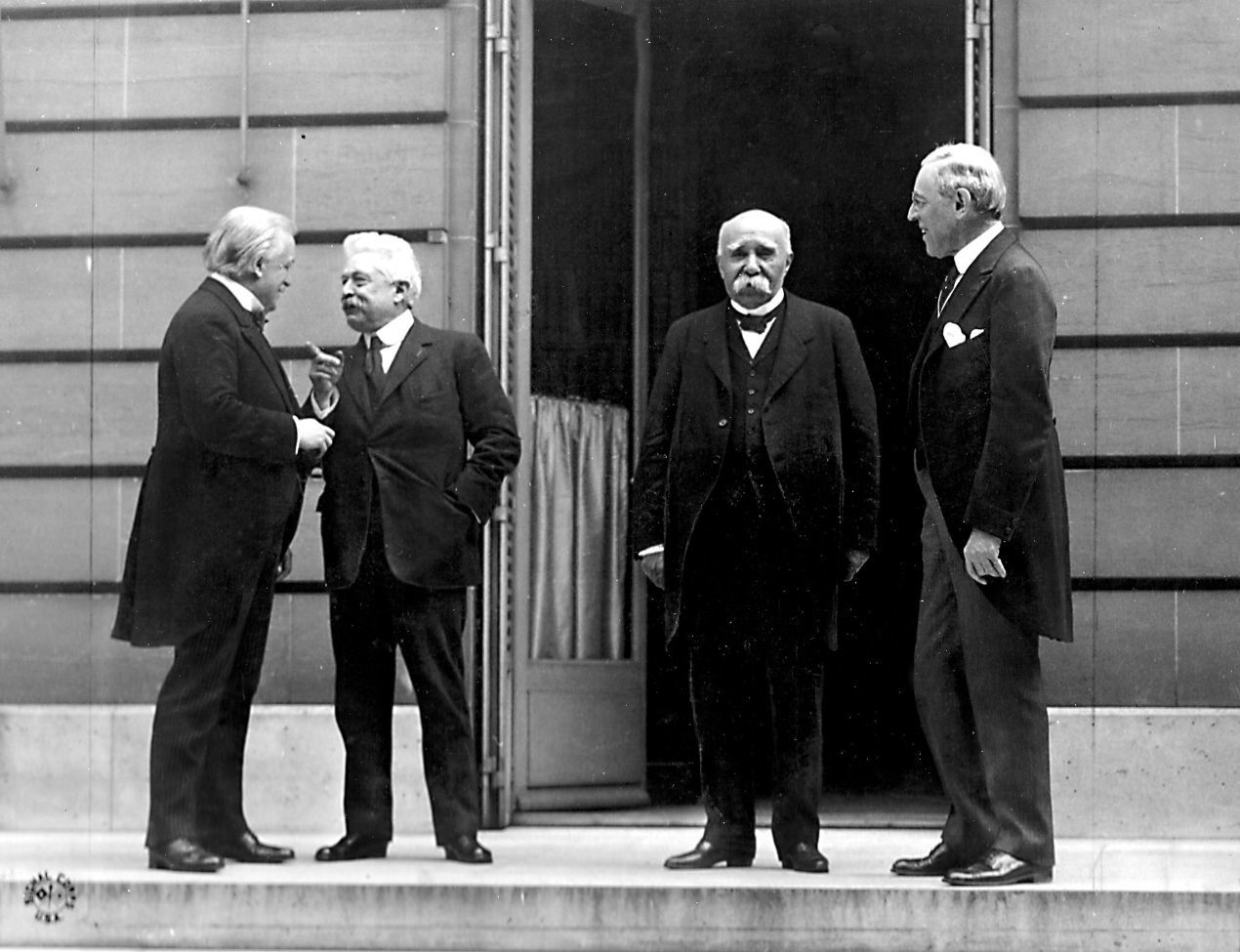

The Allied leaders at the Paris Peace Conference argued heatedly and at length about the fate of Germany and Austria. French Premier Georges Clemenceau (second from right) believed Germany would inevitably rise again and seek revenge for its defeat; he wanted the country to be stripped of land and resources, its industry destroyed, and its economy crippled. American President Woodrow Wilson (far right) on the other hand, argued for a more just and fair peace, based on the Fourteen Points, that would prevent future conflicts--although he held more resentment and animosity against Germany than he liked to admit. British Prime Minister David Lloyd-George (far left) fell in the middle; he was in favor of reparations but also wanted Germany to recover and again trade with Britain. Italian Premier Vittorio Orlando had little input on real decision-making.
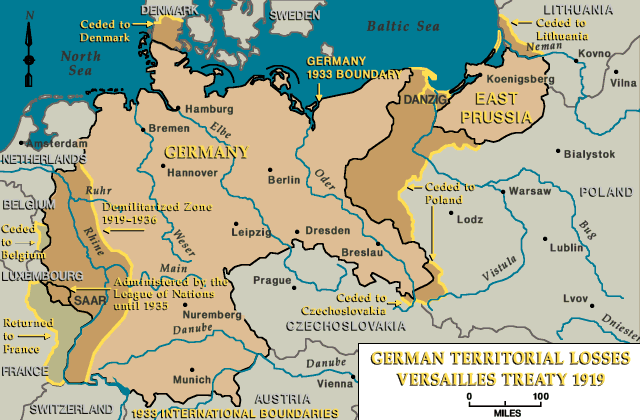
Germany lost about 13 percent of its territory after World War I. Alsace-Lorraine, at the far western edge of Germany, was returned to France; Germany had seized the provinces in 1871. The Rhineland was occupied after the war by the Allies, but despite Clemenceau's vehement arguments, it remained German territory. The Polish Corridor runs along the eastern edge of the country. You can see that it allowed the new nation of Poland access to the Baltic Sea but separated East Prussia from the rest of Germany.
This map is among the resources on the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum website,

German Foreign Minister Ulrich von Brockdorff-Rantzau made a terrible first impression on the Allies when he began by complaining that Germany was being treated unfairly. His stern and cold personality didn't help.
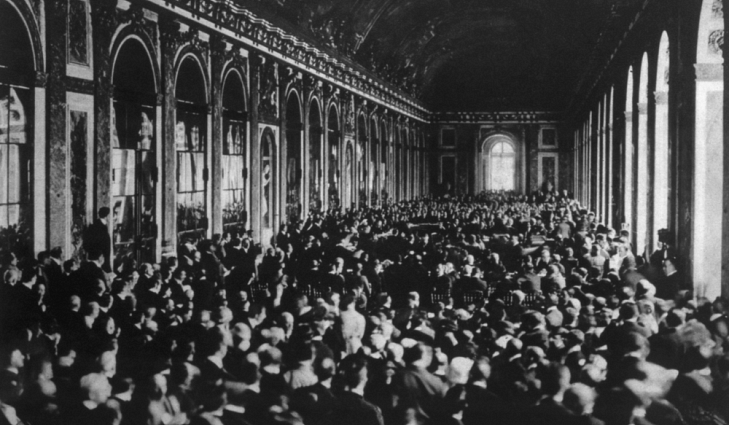

The Treaty of Versailles was signed in the Hall of Mirrors at the Palace of Versailles. The room was packed with diplomats, delegates, academic advisors, journalists, soldiers, and smattering of spies. The signing was captured by a film crew. You can watch some of the original footage on YouTube.

British economist John Maynard Keynes wrote the blockbuster bestseller The Economic Consequences of Peace in a rage after the Paris Peace Conference. He argued that the Treaty of Versailles was unjust and vindictive and would ruin the economy of Europe. Keynes' book helped convince the public that Germany had been mistreated in 1919 and deserved justice in the 1930s. Keynes went on to become one of the most influential economists of the 20th century, with an entire school of economics bearing his name.
- Please note that the links below to Amazon are affiliate links. That means that, at no extra cost to you, I can earn a commission if you click through and make a purchase. (Here's what, legally, I'm supposed to tell you: I am a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for me to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.) However, I only recommend books that I have used and genuinely highly recommend.
Links:
- Ring of Steel: Germany and Austria-Hungary in World War I by Alexander Watson — Watson describes The Great War from the perspective of the losers in this very compelling book. The detail is fantastic, giving insight into what it was like to serve on a U-Boat or work at a factory in Berlin.
- Paris 1919: Six Months That Changed the World byMargaret MacMillan — MacMillan's book is the ultimate resource on the Peace Conference. It takes an incredibly complicated series of events and makes them understandable.
- The Vanquished: Why the First World War Failed to End by Robert Gerwarth — Gerwarth takes a difficult and complicated subject and treats it with humanity and sensitivity. The book goes beyond Germany and Austria to look at events across Eastern Europe, Russia, and the Ottoman Empire.
- The World Remade: America in World War I by G. J. Meyer — The last few chapters of Meyer's book explore Wilson's actions at the Paris Peace Conference and provide insight into his mindset.
- "What if the Allies had been more generous in 1919? - Versailles revisited" by — This brief but insightful article looks at the terms of the Treaty of Versailles and asks if they were really as unjust as the Germans and Keynes claimed. (You must register with the website to read the article, but registration is free for up to five articles a month.)
27 episodes




