Eggshells Loaded with Dynamite: Allied Intervention in the Russian Revolution
Manage episode 328917896 series 3350741
In 1919, thousands of American soldiers fought Russian troops on Russian soil--despite the fact President Woodrow Wilson had promised to allow Russia to determine its own political future. Why did the Allies rush to land troops in eastern Siberia and along the Arctic Ocean? And why have we forgotten all about it?

General William S. Graves wanted to lead troops in France, but instead he was given confusing and contradictory orders and sent to Vladivostok in far eastern Siberia.

The Americans joined representatives of multiple other nations in Vladivostok, including French, British, Romanian, Serbian, Polish and Japanese troops. Many of the British units were from Canada, Australia, or New Zealand. Representatives of the Czechoslovak Legion and the White Army were also on hand. In this photo, American soldiers parade through Vladivostok shortly after their arrival in 1918.
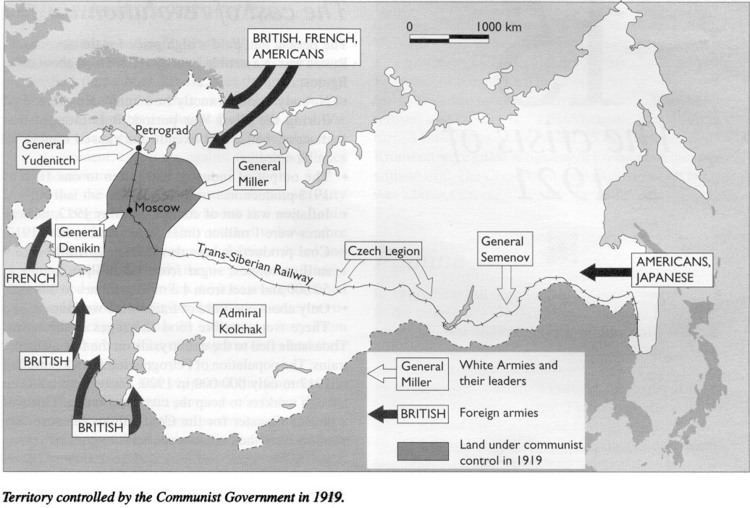
I continue to struggle to find maps that show what I want. This one shows a few key points. First, the location of the territory firmly in Bolshevik hands, land generally surrounding Moscow, is in dark gray. The route of the Trans-Siberian Railway, along which the Czechoslovak Legion seized territory, crosses Siberia. Dark arrows indicate where various Allied troops landed and tried to advance into Russia.
You'll notice arrows moving up from the South, from the Crimea and around the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea. These were primarily French and British troops, and Americans weren't involved. I haven't discussed these attempted invasions just to simplify matters.
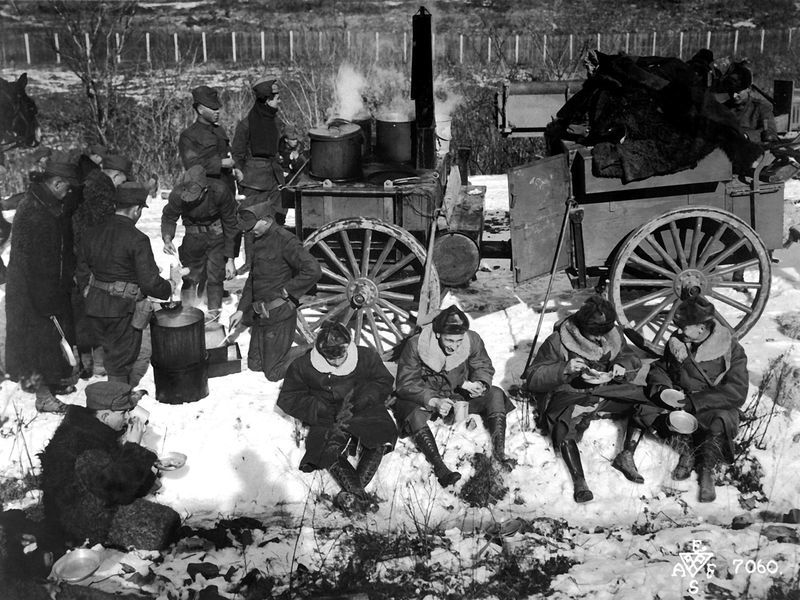

Conditions in Siberia and northern Russia were predictably harsh. This photo shows American soldiers eating while sitting on a snow bank. This looks like a relatively happy gathering; it was not usually this pleasant.

This photo gives at least an inkling how cold it was, especially in northern Russia.

Most Americans had no idea their soldiers were in Russia until the issue was picked up by Senator Hiram Johnson of California. Johnson, a Republican who despised President Wilson, made the return of the troops his number one priority in late 1918/early 1919. He hoped the issue would carry him all the way to the White House.

Johnson's pressure combined with the new-found strength of the Red Army and the general American desire to bring all of the boys home ended American intervention in Russia. Most troops in northern Russia were home by the summer of 1919. The Polar Bear Division, the 339th Infantry Regiment from Michigan, were welcomed with an enormous party in Detroit, seen here.

Japan sent more than 70,000 troops to Vladivostok. The campaign became deeply unpopular at home, in part because its purpose was unclear, in part because it was a resounding failure. In order to rally public support, Japan produced numerous propaganda images. This one shows Japanese troops landing at Vladivostok to the great joy of the Russian people. The defeat of the Japanese army in Siberia contributed to the collapse of democratic rule in Japan.
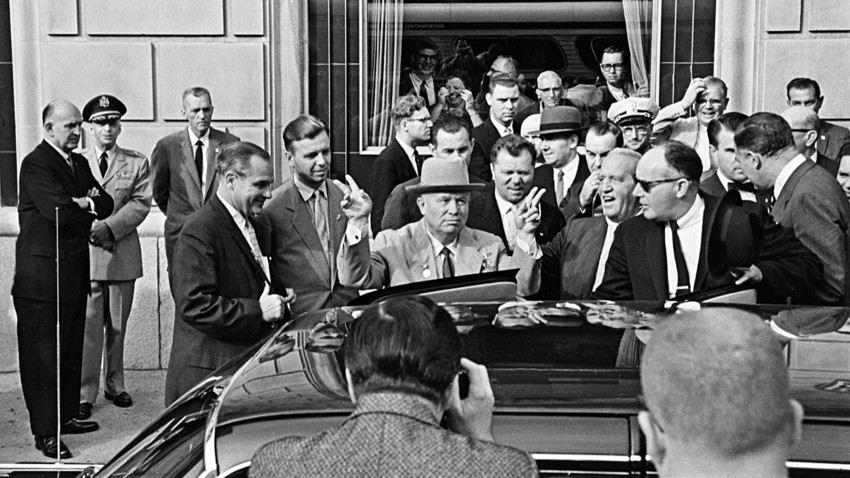

Americans might have forgotten about the Allied intervention in Russia, but the Russians certainly didn't. When Nikita Krushchev visited New York in September 1959, he pointedly brought up "the time you sent the troops to quell the revolution."
Please note that the links below to Amazon are affiliate links. That means that, at no extra cost to you, I can earn a commission if you click through and make a purchase. (Here's what, legally, I'm supposed to tell you: I am a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for me to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.) However, I only recommend books that I have used and genuinely highly recommend.
Links:
- The Polar Bear Expedition: The Heroes of America's Forgotten Invasion of Russia, 1918-1919 byJames Carl Nelson — This is a fascinating, detailed look at the Allied intervention in Russia, focusing on the Polar Bear Division from Michigan.
- Savage Peace: Hope and Fear in America, 1919 by Ann Hagedorn — Hagadorn's book has been an invaluable companion as I've worked on this season. She provides an excellent overview of the American involvement in Russia and the fight by Hiram Johnson to bring them home.
- Polar Bear Expedition History | Bentley Historical Library — This is a good overview of the Polar Bear Expedition from the Bentley Historical Library at the University of Michigan, which has assembled a collection of historical artifacts and and materials about the unit.
- "The Forgotten Story of the American Troops Who Got Caught Up in the Russian Civil War" | History | Smithsonian — This is a really solid overview of the American intervention in Russia and includes some fantastic photos.
- US Soldiers Fighting in Russia - The End of the "Polar Bear Expedition" I THE GREAT WAR May 1919 - YouTube — The Great War YouTube channel has a very good overview of the withdrawal of American troops from Russia within the context of the Russian Revolution as a whole.
- Siberian Intervention 1918-1922 | International Encyclopedia of the First World War (WW1) — This entry in the International Encyclopedia of the First World War contains interesting information about Japan's involvement Siberia and the effect on internal Japanese politics.
27 episodes




